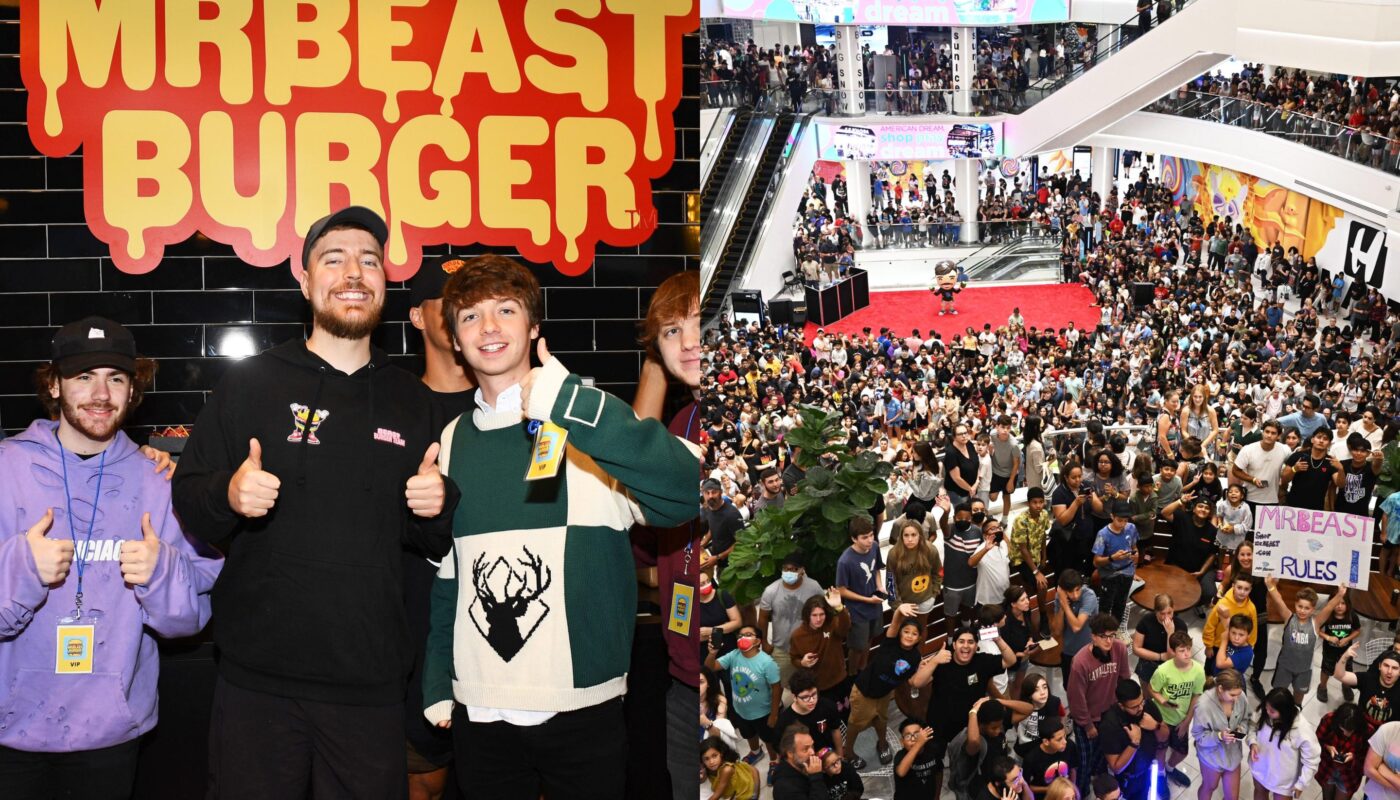
Overview of MrBeast’s Business Empire: Restaurants
The rise of MrBeast from YouTube creator to entrepreneur illustrates a modern media-to-market phenomenon. Among his most notable ventures is MrBeast’s Business Empire: Restaurants, a collection of food-related businesses that blend digital influence with real-world dining. Often referred to as MrBeasts restaurant ventures or the MrBeast dining empire, these initiatives span virtual kitchens, delivery-first concepts, pop-ups, and select brick-and-mortar locations. The common denominator is a focus on brand, scalability, and, of course, tapping into attention-driven demand that translates to money and revenue.
Origins and Early Growth
From content to commerce
The first forays into food business for MrBeast leveraged his enormous online audience. By pairing virality with a simple, repeatable menu, the team behind MrBeast’s Business Empire: Restaurants could launch with low overhead. The initial model was a classic example of the “influencer-first” product rollout: create hype, convert followers into customers, iterate quickly.
Ghost kitchens and partnerships
One of the earliest effective strategies was the use of ghost kitchens or virtual restaurants. Instead of immediately leasing dozens of storefronts, MrBeast’s teams partnered with existing restaurants and kitchen networks to prepare food under the brand name, typically for delivery platforms. This approach reduced capital expenditure while enabling rapid geographic scaling and quick testing of market demand.
Business Model: How the Restaurant Empire Makes Money
The business architecture of MrBeast’s restaurant ventures is designed around several revenue and profit levers that exploit the strengths of modern foodservice economics and influencer marketing:
- Brand-driven pricing: Fans are often willing to pay a premium for novelty and association with a creator they trust.
- Low fixed costs: By using third-party kitchens and delivery platforms, initial fixed costs are minimized.
- High marketing efficiency: Organic reach from social channels lowers customer acquisition costs compared to traditional restaurant marketing.
- Multiple revenue streams: Direct sales (delivery and dine-in), branded merchandise, licensing and partnerships, and cross-promotion with other MrBeast businesses.
Unit economics and margins
Although specific numbers vary by region and concept, the core economics revolve around:
- Average order value (AOV): Influenced by bundling, upsells, and premium items.
- Food cost percentage: Typically a primary determinant of profitability; the brand often designs menus with standardized ingredients to control costs.
- Delivery commissions: Platform fees can erode margins, which is why optimizing order size and direct-to-consumer channels is important.
- Marketing ROAS: Return on ad spend is replaced by organic reach metrics thanks to the creator’s audience.
Flagship Concepts and Menu Strategy
Within the broader MrBeast dining empire, signature concepts emphasize simplicity and viral appeal. Typical menu design principles include:
- Limited but distinctive offerings: One or two star items (e.g., burgers, fries, shakes) that can be executed consistently.
- Cross-promotional items: Meal combos named after events or giveaways to spur social sharing.
- Merch and add-on sales: Branded snacks, collectibles, and packaged goods sold alongside meals or online.
These menu strategies create operational efficiency while enabling the brand to leverage its cultural cachet. A recognizable menu helps reduce customer decision friction and speeds up kitchen throughput — essential for delivery-heavy concepts.
Expansion Strategy: Scaling the MrBeast Burger Business
Phased rollout
Expansion typically follows a phased approach:
- Pilot markets via virtual kitchens and pop-ups;
- Regional scale using partnerships with restaurant groups and kitchen networks;
- Selective brick-and-mortar locations in high-visibility markets to serve as flagship experiences and PR magnets;
- International licensing where local partners replicate the model under license or franchise agreements.
Franchises, licenses, and partnerships
For rapid growth, the empire uses a mix of:
- Franchise agreements to transfer operational standards to local operators;
- Licensing deals that allow third parties to use the brand in exchange for fees and royalties;
- White-label partnerships where existing restaurants produce menu items under the MrBeast brand for delivery channels.
Marketing, Social Currency, and Revenue Multipliers
One of the most powerful advantages of MrBeast’s Business Empire: Restaurants is the inherent marketing engine. Social media posts, video content, and high-profile stunts generate attention that translates directly into sales. The interplay between content and commerce creates several revenue multipliers:
- Earned media: News coverage and viral posts reduce paid marketing spend.
- Lifetime value (LTV) uplift: Fans often make repeat purchases driven by loyalty and novelty.
- Cross-sales: Food ventures can introduce customers to other products like snacks and merchandise, increasing overall customer lifetime revenue.
Financial Footprint and Money Flow
While exact financial statements for the overall restaurant operations may not be publicly disclosed in full detail, common financial elements for the empire include:
- Upfront fees and capital: Initial investments for menu development, branding, and logistics integration;
- Ongoing royalties: For franchises and licensees paying a percentage of gross sales back to the brand;
- Merchant margins: Net earnings after food costs, labor, rent (if applicable), and delivery commissions;
- Ancillary income: Merchandise sales, brand partnerships, sponsorships, and media deals that flow into the parent company.
The business often optimizes for cash flow by minimizing fixed assets early on and capturing cash from deliveries and merchandise sales quickly, accelerating reinvestment into expansion and marketing.
Operational Challenges and Risk Management
Quality control and consistency
Scaling through third-party kitchens introduces variability. Ensuring consistent food quality across hundreds of locations is a perpetual challenge. Standardized recipes, training modules, and mystery-shop audits are common mitigations.
Platform dependence and fees
Heavy reliance on delivery platforms exposes the restaurant empire to commission hikes and policy changes. Diversifying fulfillment channels, encouraging direct orders, and negotiating preferred rates are typical strategies to protect margins.
Reputation risk
As with any influencer-led brand, public controversies or operational missteps can rapidly affect demand. Transparent communication and customer service responsiveness are critical elements of risk management for a high-profile food brand.
Broader Impact on the Fast-Casual Sector
The MrBeast dining empire has influenced how investors, creators, and restaurant operators think about growth. Key ripple effects include:
- Creator-led brands becoming credible players: Other content creators now see foodservice as an attractive vertical;
- Acceleration of ghost kitchen adoption: The model validated the speed and scale possible with delivery-first concepts;
- New customer acquisition channels: Social-first launches reduce reliance on traditional restaurant marketing budgets;
- Increased competition for delivery market share: Established chains and independents must adapt to branded virtual entrants.
Case Studies and Notable Launches
Within the umbrella of MrBeast’s Business Empire: Restaurants, specific launches have served as case studies for modern restaurant commercialization:
- Delivery-first burger concept: A high-velocity menu that relied on social media to populate early orders and gather feedback;
- Limited-time pop-ups: In-person experiences that generated content, drove local awareness, and tested markets;
- Branded product rollouts: Snack and beverage offerings that extended the brand beyond prepared meals and into retail channels.
Legal, Regulatory, and Ethical Considerations
Operating a restaurant empire at scale brings compliance requirements: food safety, labor law adherence, and accurate advertising practices. For a brand where public trust is a key asset, aligning operations with both legal standards and audience expectations is essential. Ethical considerations include fair pay for partner kitchens and responsible marketing to avoid misleading claims about health or sourcing.
What Comes Next for MrBeast’s Restaurant Businesses
Predicting the trajectory of MrBeast’s restaurant ventures involves examining a few likely vectors:
- Deeper retail presence: More packaged goods and supermarket placements to diversify income;
- Permanent flagship stores: High-profile locations that serve as experience centers and content backdrops;
- Global franchising: Local operators adapting the brand to regional tastes while paying royalties and fees;
- Tech integration: Direct ordering apps, loyalty programs, and data-driven menu optimization to reduce reliance on third-party platforms.
The evolving interplay of attention economy, operational discipline, and financial engineering will determine whether the dining ventures remain a high-margin novelty, a robust multi-channel food business, or a hybrid model that reshapes expectations for influencer-led enterprises. Stakeholders — from investors to kitchen staff — will be watching benchmarks like same-store sales growth, average ticket size, and the percentage of revenue derived from non-food channels as signals of long-term viability as part of the broader